Scientists Accidentally Develop ‘Mutant’ Enzyme That Eats Plastic
ENVIRONMENT, 23 Apr 2018
Lorraine Chow | EcoWatch – TRANSCEND Media Service
17 Apr 2018 – Researchers in the UK and the U.S. have inadvertently engineered an enzyme that eats up plastic.
The enzyme is able to digest PET (polyethylene terephthalate)—the same material used in the ubiquitous plastic bottle that’s clogging up landfills, coastlines and oceans around the world.
Amazingly, this discovery only happened by chance. Scientists from the University of Portsmouth in the UK and the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) were examining the structure of a natural enzyme, Ideonella sakaiensis, found in 2016 at a Japanese waste recycling center. This enzyme could already break down PET plastic—it just doesn’t do it very quickly.
To understand how Ideonella sakaiensis evolved, the research team “tweaked” the structure of the enzyme by adding some amino acids, according to John McGeehan, a Portsmouth professor who co-led the work. They ended up creating an enzyme that worked even faster than the natural one.
“Surprisingly, we found that the PETase mutant outperforms the wild-type PETase in degrading PET,” said NREL materials scientist Nic Rorrer.
McGeehan added, “Serendipity often plays a significant role in fundamental scientific research and our discovery here is no exception.”
The modified enzyme, called PETase, can break down PET in just a few days—a stunning discovery that could help fight the world’s escalating plastic crisis.
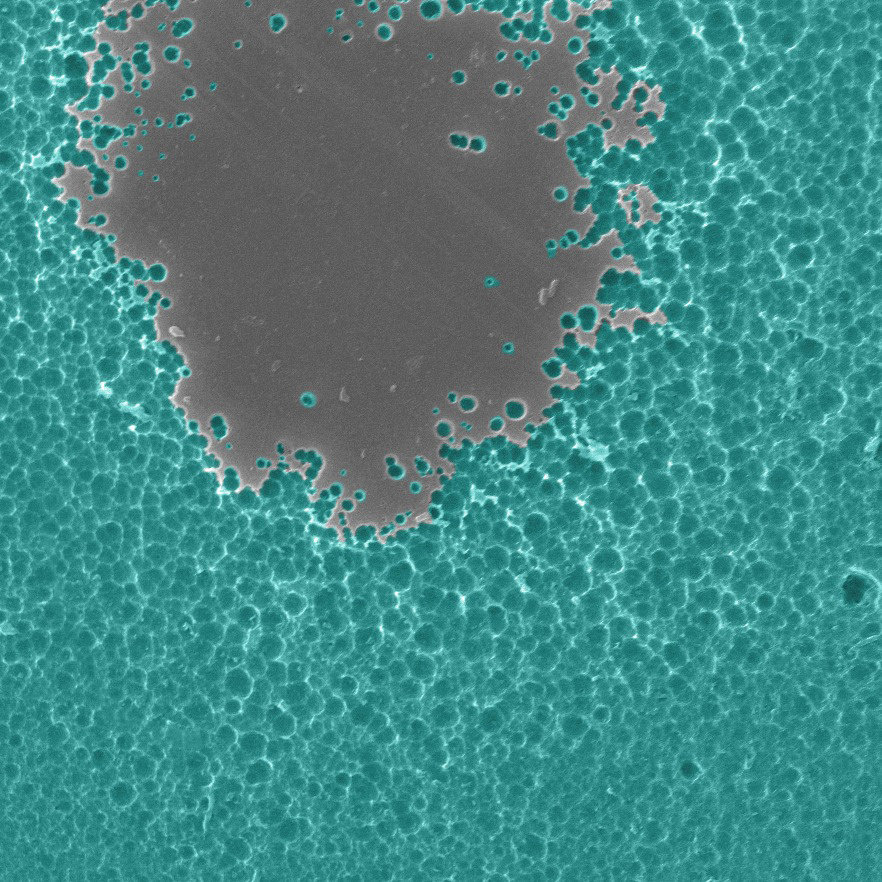
“After just 96 hours you can see clearly via electron microscopy that the PETase is degrading PET,” said NREL structural biologist Bryon Donohoe.
“And this test is using real examples of what is found in the oceans and landfills.”
As BBC News explained, PETase works by reversing the manufacturing process by reducing polyesters back to their building blocks so it can be used again.
When you drink soda, water or juice from a plastic bottle, those bottles are almost never made from recycled plastic. Additionally, as the Guardian noted, the plastic bottles that do get recycled can only be turned into polyester fibers for carpet or fabric.
But this new finding suggests a way to turn plastic bottles back into plastic bottles.
“They could be used to make more plastic and that would avoid using any more oil … Then basically we’d close the loop. We’d actually have proper recycling,” McGeehan told BBC News.
The team’s finding was published Monday in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The researchers are now working to improve PETase to see if it can work on an industrial scale. About one million plastic bottles are purchased around the world every minute, with that number predicted to increase another 20 percent by 2021.
“This unanticipated discovery suggests that there is room to further improve these enzymes, moving us closer to a recycling solution for the ever-growing mountain of discarded plastics,” McGeehan said.
How Best to Rid the World's Oceans of Plastic? https://t.co/nQD4D3Y2hg @ShaunFrankson @Surfrider
— EcoWatch (@EcoWatch) May 16, 2017
__________________________________________________
 Lorraine Chow is a reporter for EcoWatch.
Lorraine Chow is a reporter for EcoWatch.
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.