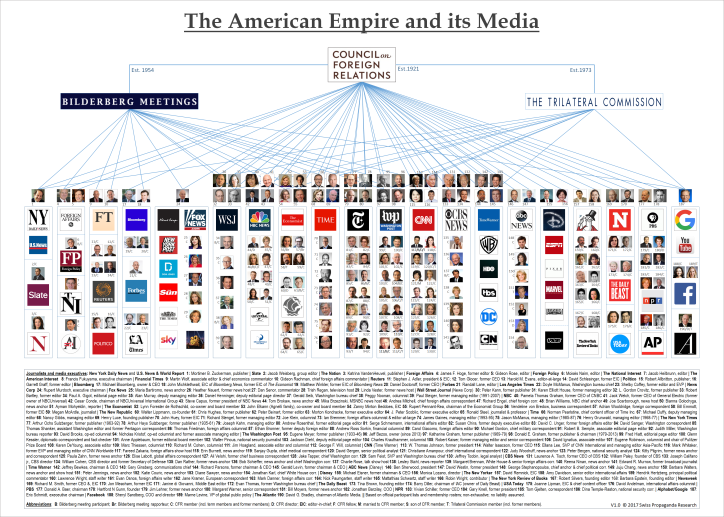
Largely unbeknownst to the general public, executives and top journalists of almost all major US media outlets have long been members of the influential Council on Foreign Relations (CFR).
19 March 2020 – Established in 1921 as a private, bipartisan organization to “awaken America to its worldwide responsibilities”, the CFR and its close to 5000 elite members for decades have shaped US foreign policy and public discourse about it. As a well-known Council member famously explained, they transformed the American republic into a global empire, albeit a “benevolent” one.
Based on official membership rosters, the following illustration depicts for the first time the extensive media network of the CFR and its two major international affiliate organizations: the Bilderberg Group (mainly covering the US and Europe) and the Trilateral Commission (covering North America, Europe and East Asia), both established by Council leaders to foster elite cooperation at the global level.
In a column entitled “Ruling Class Journalists”, former Washington Post senior editor and ombudsman Richard Harwood described the Council and its members approvingly as “the nearest thing we have to a ruling establishment in the United States”.
Harwood continued: “The membership of these journalists in the Council, however they may think of themselves, is an acknowledgment of their active and important role in public affairs and of their ascension into the American ruling class. They do not merely analyze and interpret foreign policy for the United States; they help make it. (…) They are part of that establishment whether they like it or not, sharing most of its values and world views.”
However, media personalities constitute only about five per cent of the overall CFR network. As the following illustration shows, key members of the private Council on Foreign Relations have included:
- several US Presidents and Vice Presidents of both parties;
- almost all Secretaries of State, Defense, and the Treasury;
- many high-ranking commanders of the US military and NATO;
- some of the most influential Members of Congress (notably in foreign & security policy);
- almost all National Security Advisors, CIA Directors, Ambassadors to the U.N., Chairs of the Federal Reserve, Presidents of the World Bank, and Directors of the National Economic Council;
- many prominent academics, especially in key fields such as Economics and Political Science;
- many top executives of Wall Street, policy think tanks, universities, NGOs, and Hollywood;
- as well as the key members of both the 9/11 Commission and the Warren Commission (JFK)
Harvard economist and Kennedy supporter, John K. Galbraith, confirmed the Council’s influence: “Those of us who had worked for the Kennedy election were tolerated in the government for that reason and had a say, but foreign policy was still with the Council on Foreign Relations people.”
Princeton University professor and former CFR member Stephen F. Cohen described the Council as “America’s single most important non-governmental foreign-policy organization”, whose primary role is to “define the accepted, legitimate, orthodox parameters of discussion.” According to Cohen, “the CFR really is what the Soviets used to call the very top-level of the Nomenklatura.”
And no less than John J. McCloy, the longtime chairman of the Council and advisor to several US presidents, recalled about his time in Washington: “Whenever we needed a man, we thumbed through the roll of the Council members and put through a call to New York [i.e., the CFR headquarters].”
German news magazine Der Spiegel once described the CFR as the “most influential private institution of the United States and the Western world” and a “politburo of capitalism”. Both the Roman-inspired logo of the Council (top right in the illustration above), as well as its slogan (ubique – omnipresent), appear to emphasize this ambition.
In his famous article about “The American Establishment”, political columnist Richard H. Rovere noted: “The directors of the CFR make up a sort of Presidium for that part of the Establishment that guides our destiny as a nation. (…) [I]t rarely fails to get one of its members, or at least one of its allies, into the White House. In fact, it generally is able to see to it that both nominees are men acceptable to it.”
Until recently, this assessment indeed was justified. Thus, in 1993 former CFR director George H.W. Bush was followed by CFR member Bill Clinton, who in turn was followed by CFR “family member” George W. Bush.
In 2008, CFR member John McCain lost against CFR candidate of choice, Barack Obama, who received the names of his entire Cabinet already one month prior to his election by CFR Senior Fellow (and Citigroup banker) Michael Froman. Froman later negotiated the TPP and TTIP trade agreements, before returning to the CFR as a Distinguished Fellow.
It was not until the 2016 election that the Council couldn’t, apparently, prevail. At any rate, not yet.
∗∗∗
Update 2018: In January 2018, a few weeks before his internet access was cut off, WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange shared the above CFR media chart on his Twitter account.
Update 2019: It became known that deceased billionaire sex trafficker Jeffrey Epstein had been, until 2009, a member and donor of both the Council on Foreign Relations and the Trilateral Commission.


[…] ruling elites can be found in powerful semi-covert networks such as the World Economic Forum, the Council on Foreign Relations, and the Trilateral Commission. They include top financiers, as described by Peter Phillips in […]