The United Nations and Decolonization: Non-Self-Governing Territories
UNITED NATIONS, 12 Oct 2020
The United Nations - TRANSCEND Media Service
Under Chapter XI of the Charter of the United Nations, the Non-Self-Governing Territories are defined as “territories whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government”.
The General Assembly, by its resolution 66 (I) of 14 December 1946, noted a list of 72 Territories to which Chapter XI of the Charter applied.
In 1963, the Special Committee on the Situation with regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples (also known as the “Special Committee on Decolonization” or the “C-24”) approved a preliminary list of Territories to which the Declaration applied (A/5446/Rev.1, annex I).
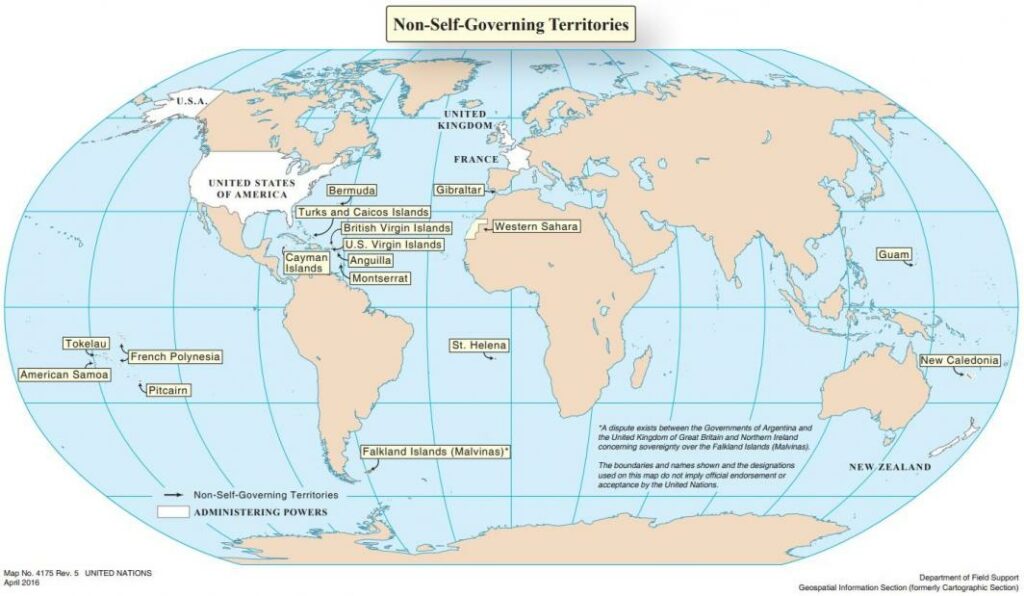
Today, 17 Non-Self-Governing Territories, as listed below, remain on the agenda of the C-24. Member States which have or assume responsibilities for the administration of such Territories are called administering Powers.
Last updated: 22 Sep 2020
LIST OF NON-SELF-GOVERNING TERRITORIES BY REGION
| TERRITORY | LISTING AS NSGT | ADMINISTERING POWER | LAND AREA (sq.km.) | POPULATION [i] |
|
AFRICA |
||||
| Western Sahara | Since 1963 | [ii] | 266,000 | 582,000 |
|
ATLANTIC AND CARIBBEAN |
||||
| Anguilla | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 96 | 15,397 |
| Bermuda | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 53.35 | 63,921 |
| British Virgin Islands | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 153 | 31,197 |
| Cayman Islands | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 264 | 65,813 |
| Falkland Islands (Malvinas) [iii] | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 12,173 | Approximately 3,200 |
| Montserrat | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 103 | 4,649 |
| Saint Helena | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 310 | 5,467 |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 948.2 | 42,953 |
| United States Virgin Islands | Since 1946 | United States | 352 | 105,000 |
|
EUROPE |
||||
| Gibraltar | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 5.8 | 34,003 |
|
PACIFIC |
||||
| American Samoa | Since 1946 | United States | 200 | 60,300 |
| French Polynesia | 1946-1947 and since 2013 | France | 3,600 | 276,300 |
| Guam | Since 1946 | United States | 540 | 163,875 |
| New Caledonia | 1946-1947 and since 1986 | France | 18,575 | 268,767 |
| Pitcairn | Since 1946 | United Kingdom | 35.5 | 43 |
| Tokelau | Since 1946 | New Zealand | 12.2 | 1,499 |
NOTES:
[i] All data is from United Nations Secretariat 2020 Working Papers on Non-Self-Governing Territories, and for Western Sahara, from UNdata, a database by the United Nations Statistics Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations.
[ii] On 26 February 1976, Spain informed the Secretary-General that as of that date it had terminated its presence in the Territory of the Sahara and deemed it necessary to place on record that Spain considered itself thenceforth exempt from any responsibility of any international nature in connection with the administration of the Territory, in view of the cessation of its participation in the temporary administration established for the Territory. In 1990, the General Assembly reaffirmed that the question of Western Sahara was a question of decolonization which remained to be completed by the people of Western Sahara.
[iii] A dispute exists between the Governments of Argentina and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland concerning sovereignty over the Falkland Islands (Malvinas).
Tags: Colonialism, Colonization, Decolonization, Neocolonialism, Occupation, United Nations
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.