How We Can Fix This Pandemic in a Month
COVID19 - CORONAVIRUS, 6 Jul 2020
Damien Downing, MBBS, MRSB | Orthomolecular Medicine News Service - TRANSCEND Media Service
22 Jun 2020 – If we act on the data showing that it is highly probable that vitamin D can save lives, we could fix this pandemic in a month, for perhaps $2 per person. There would be no significant adverse effects. If we wait for “evidence” that vitamin D mitigates the impact of COVID-19, thousands more will die. If we could arrange to give everyone vitamin D, and it failed to protect them, so what? The risk from not acting is much greater than the risk from acting. Dosage is important and generally misunderstood.
Two countries have acted on this already: Egypt and Slovakia. Why can’t we?
The Orthomolecular Medicine News Service has been publicizing the importance of vitamins D and C, and the minerals zinc and magnesium, in this pandemic since January [1]. I have been writing about Vitamin D and sunlight for over 30 years [2], and it has never been more relevant.
If you caught the COVID19 virus right now, having a good vitamin D status (from already having taken a supplement) would
- Reduce your risk of the disease becoming severe by 90%
- Reduce your risk of dying by 96%
This is not “proven” or “evidence-based” until we have done controlled trials comparing it to placebo. Any volunteers for that? But the data, already strong, has been pouring in since the start of the pandemic. Here’s the data for the two statements above.
[A Hazard Ratio of 4 means that in one condition, for instance vitamin D deficiency, you are 4 times more likely to suffer the “hazard” than in another condition, say vitamin D adequacy. The graphics are all mine.]
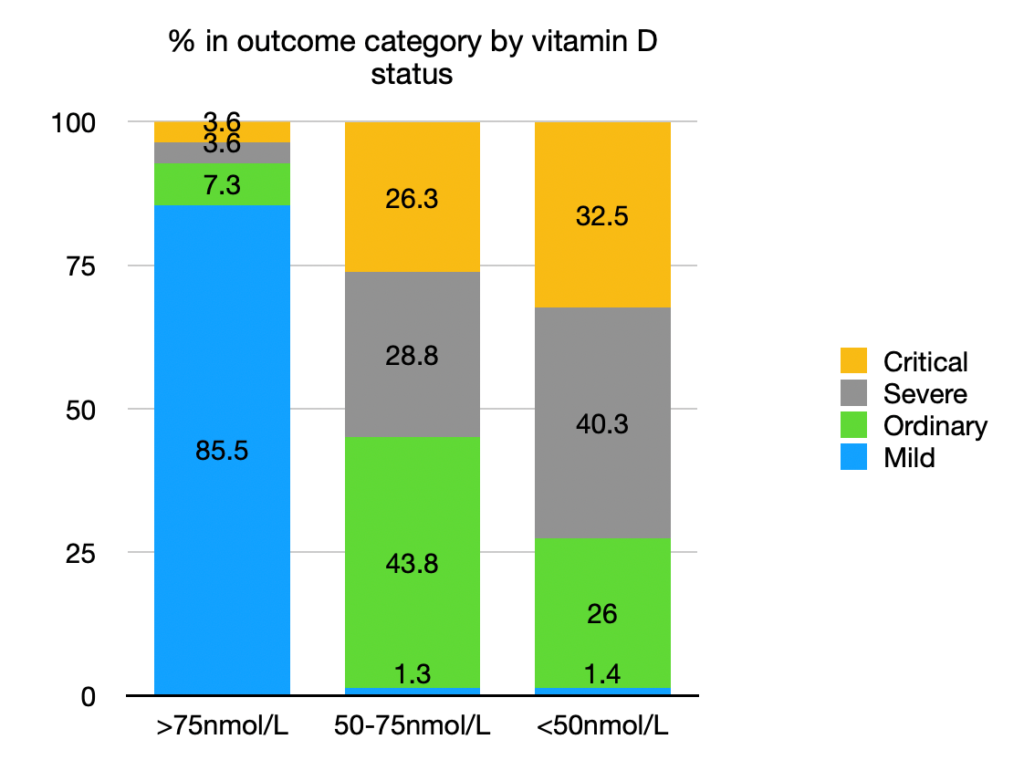
A Philippine study [3]
With a deficient vitamin D status (<50nmol/L) the probability of becoming Severe or Critical with COVID-19 was 72.8% against 7.2% with adequate vitamin D (>75nmol/L). The Hazard Ratio is 10.0.
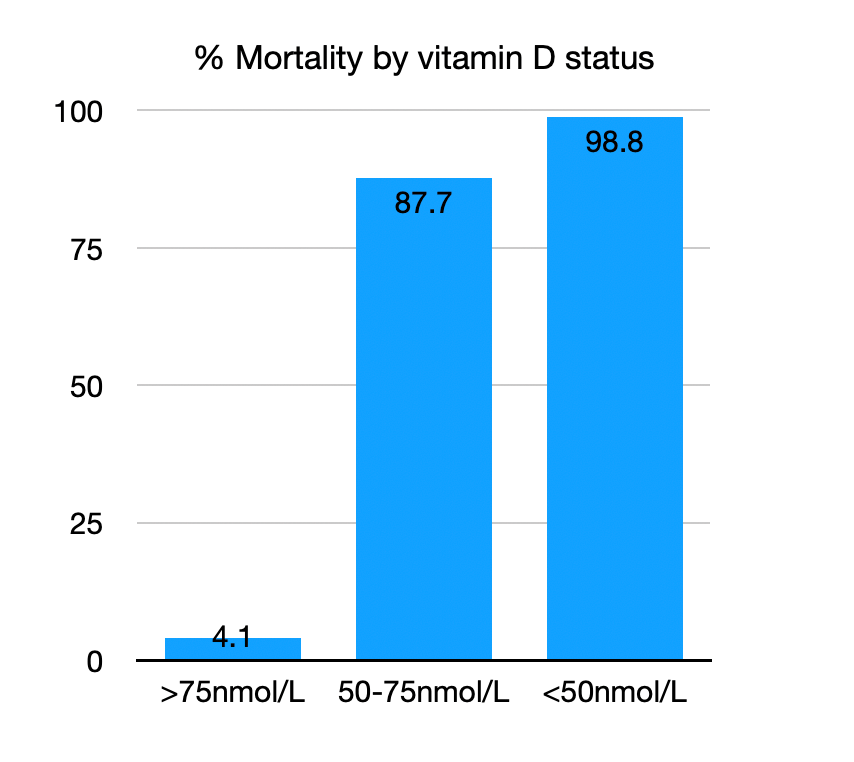
An Indonesian study [4]
With a deficient vitamin D status (<50nmol/L) the mortality rate from COVID-19 was 98.8% against 4.1% with adequate vitamin D (>75nmol/L). The Hazard Ratio is 24.1.
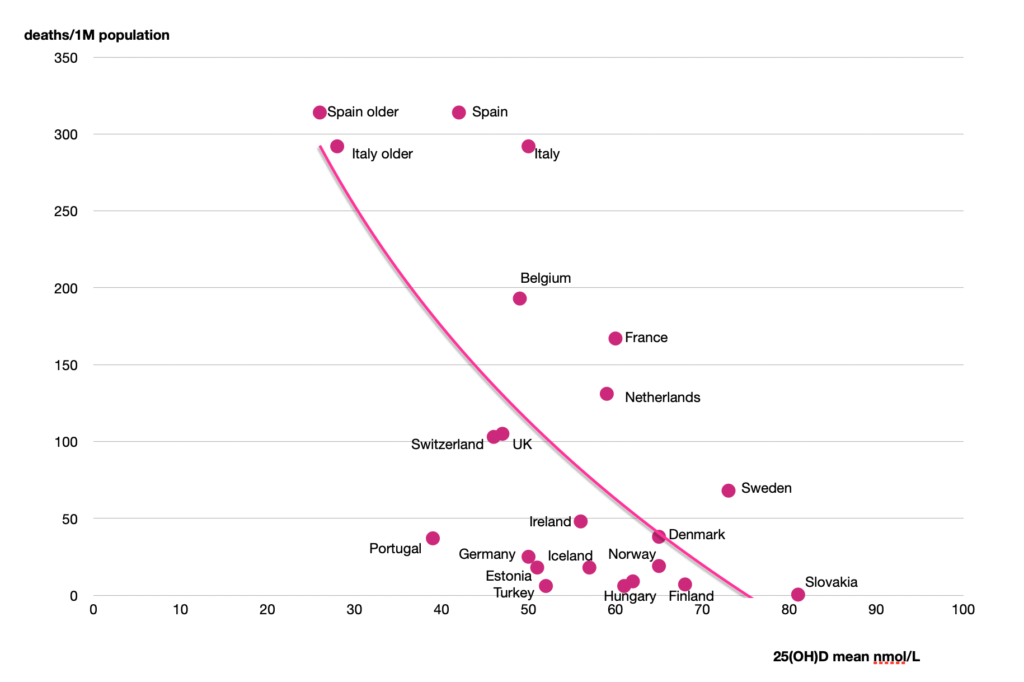
A review of data on Europe [5]
For countries in Europe, the probability of developing COVID-19, and of dying from it, is negatively correlated with mean population vitamin D status, with both probabilities reaching zero above about 75nmol/L. (The chart also shows the lower vitamin D levels for the elderly in Spain and Italy. [6]) It is also known that other factors such as age, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes are commonly associated with death in COVID-19. [5-8] For example, the elderly population in care facilities often do not get much sunlight exposure nor adequate supplements of essential nutrients including vitamin D, which will increase their risk of serious infections. Further, the 25(OH)D level in northern European countries such as Sweden drops in late winter to ~50 nmol/L or less, which may explain their relatively high death rate from infection. [9]
Dosage is important and generally misunderstood
Recent studies have suggested in discussion that more than 4000 IU per day of vitamin D3 may carry a risk of harm, citing the UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition report of 2016 which set the recommended Upper Level (UL) intakes of 50mcg/2000IU per day. [10] That report says; “Excessive vitamin D intakes have, however, been shown to have toxic effects (Vieth, 2006)”. [10] However this is misleading, as the Vieth paper [11] states: “Published reports suggest toxicity may occur with 25(OH)D concentrations beyond 500 nmol/L.” This leaves a wide margin of safety.
The 3 papers mentioned above [3-5] show that a vitamin D3 blood level of at least 75 nmol/L (30 ng/ml) is needed for protection against COVID-19. Government recommendations for vitamin D intake – 400 IU/day for the UK and 600 IU/day for the USA (800 IU for >70 years) and the EU – are based primarily on bone health. This is woefully inadequate in the pandemic context. An adult will need to take 4000 IU/day of vitamin D3 for 3 months to reliably achieve a 75 nmol/L level [12]. Persons of color may need twice as much [13]. These doses can reduce the risk of infection, but are not for treatment of an acute viral infection. And since vitamin D is fat-soluble and its level in the body rises slowly, for those with a deficiency, taking a initial dose of 5-fold the normal dose (20,000 IU/day) for 2 weeks can help to raise the level up to an adequate level to lower infection risk.
Other essential nutrients can help
As mentioned above, many studies have shown that for those deficient in essential nutrients, a protocol that includes vitamin D, vitamin C, magnesium, and zinc can decrease the risk of infection for viruses, including those similar to COVID-19.[1] Recommended preventive adult doses are vitamin C, 3000 mg/day (in divided doses, to bowel tolerance), magnesium, 400 mg (in malate, citrate, or chloride form), zinc, 20 mg. [1]
References:
1. Saul AW. (2020) Vitamin C Protects Against Coronavirus. Orthomolecular Medicine News Service http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n04.shtml
2. Downing D. (1988) Day Light Robbery. Arrow Books, London. ISBN-13: 978-0099567400
3. Alipio MM. (2020) Vitamin D supplementation could possibly improve clinical outcomes of patients infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID- 2019). Preprint available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3571484
4. Raharusuna P, Priambada S, Budiarti C et al. (2020) Patterns of COVID-19 Mortality and Vitamin D: An Indonesian Study.
5. Ilie, P., Stefanescu, S., Smith, L. (2020) The role of Vitamin D in the prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 infection and mortality. Research Square preprint. https://europepmc.org/article/ppr/ppr147305
6. Lips P, Cashman K, Lamberg-Allardt C et al (2019) Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society. Eur J Endocrinol. 180:23-54. https://europepmc.org/article/MED/30721133
7. Oaklander M (2020) Almost Every Hospitalized Coronavirus Patient Has Another Underlying Health Issue, According to a Study of New York Patients. Time Magazine, April 22, 2020. https://time.com/5825485/coronavirus-risk-factors
8. Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M. (2020) Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 323:2052-2059. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2765184
9. Klingberg E, Oleröd G, Konar J, et al. (2015) Seasonal variations in serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in a Swedish cohort. Endocrine, 49:800-808. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25681052
10. UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) (2016) Vitamin D and Health. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/537616/SACN_Vitamin_D_and_Health_report.pdf
11. Vieth R (2006) Critique of the considerations for establishing the tolerable upper intake level for vitamin D: critical need for revision upwards. J Nutr, 136:1117-1122. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16549491
12. Vieth R, Chan PC, MacFarlane GD. (2001) Efficacy and safety of vitamin D(3) intake exceeding the lowest observed adverse effect level. Am J Clin Nutr, 73:288-294. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11157326
13. Cashman KD, Ritz C, Adebayo FA, et al. (2019) Differences in the dietary requirement for vitamin D among Caucasian and East African women at Northern latitude. Eur J Nutr. 58:2281-2291. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30022296
__________________________________________________
 Orthomolecular medicine uses safe, effective nutritional therapy to fight illness. For more information: http://www.orthomolecular.org
Orthomolecular medicine uses safe, effective nutritional therapy to fight illness. For more information: http://www.orthomolecular.org
The peer-reviewed Orthomolecular Medicine News Service is a non-profit and non-commercial informational resource.
Comments and media contact: drsaul@doctoryourself.com
Go to Original – orthomolecular.org
Tags: COVID-19, Coronavirus, Pandemic, Vitamin C, Vitamin D
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.
Read more
Click here to go to the current weekly digest or pick another article:
COVID19 - CORONAVIRUS: