An NSA-Derived Ransomware Worm Is Shutting Down Computers Worldwide
TECHNOLOGY, 15 May 2017
Dan Goodin | Ars Technica – TRANSCEND Media Service
Wcry uses weapons-grade exploit published by the NSA-leaking Shadow Brokers.
12 May 2017 – A highly virulent new strain of self-replicating ransomware shut down computers all over the world, in part by appropriating a National Security Agency exploit that was publicly released last month by the mysterious group calling itself Shadow Brokers.
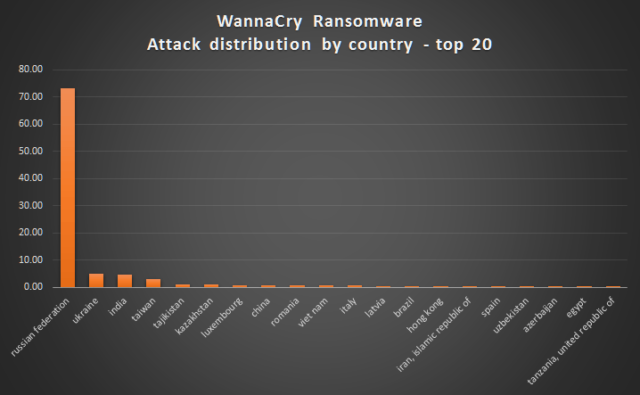
The malware, known as Wanna, Wannacry, or Wcry, has infected at least 75,000 computers, according to antivirus provider Avast. AV provider Kaspersky Lab said organizations in at least 74 countries have been affected, with Russia being disproportionately affected, followed by Ukraine, India, and Taiwan. Infections are also spreading through the United States. The malware is notable for its multi-lingual ransom demands, which support more than two-dozen languages.
Wcry is reportedly causing disruptions at banks, hospitals, telecommunications services, train stations, and other mission-critical organizations in multiple countries, including the UK, Spain, Germany, and Turkey. FedEx, the UK government’s National Health Service, and Spanish telecom Telefonica have all been hit. The Spanish CERT has called it a “massive ransomware attack” that is encrypting all the files of entire networks and spreading laterally through organizations.
The virally spreading worm was ultimately stopped when a researcher who uses the Twitter handle MalwareTech and works for security firm Kryptos Logic took control of a domain name that was hard-coded into the self-replicating exploit. The domain registration, which occurred around 6 AM California time, was a major stroke of good luck, because it was possible only because the attackers had failed to obtain the address first.
The address appeared to serve as a sort of kill switch the attackers could use to terminate the campaign. MalwareTech’s registration had the effect of ending the attacks that had started earlier Friday morning in other parts of the world. As a result, the number of infection detections plateaued dramatically in the hours following the registration. It had no effect on WCry infections that were initiated through earlier campaigns.
Remember Code Red?
Another cause for concern: wcry copies a weapons-grade exploit codenamed Eternalblue that the NSA used for years to remotely commandeer computers running Microsoft Windows. Eternalblue, which works reliably against computers running Microsoft Windows XP through Windows Server 2012, was one of several potent exploits published in the most recent Shadow Brokers release in mid-April. The Wcry developers have combined the Eternalblue exploit with a self-replicating payload that allows the ransomware to spread virally from vulnerable machine to vulnerable machine, without requiring operators to open e-mails, click on links, or take any other sort of action.
So-called worms, which spread quickly amid a chain of attacks, are among the most virulent forms of malware. Researchers are still investigating how Wcry takes hold. The awesome power of worms came to the world’s attention in 2001 when Code Red managed to infect more than 359,000 Windows computers around the world in 14 hours.
“The initial infection vector is something we are still trying to find out,” Adam Kujawa, a researcher at antivirus provider Malwarebytes, told Ars. “Considering that this attack seems targeted, it might have been either through a vulnerability in the network defenses or a very well-crafted spear phishing attack. Regardless, it is spreading through infected networks using the EternalBlue vulnerability, infecting additional unpatched systems.”
It’s not clear if the Eternalblue exploit is Wcry’s sole means of spreading or if it has multiple methods of propagating. In an update that was notable for its unlikely and extremely fortuitous timing, Microsoft patched the underlying vulnerability in March, exactly four weeks before the Shadow Brokers’ April release published the weapons-grade NSA exploit. The rapid outbreak of Wcry may be an indication that many, or possibly all, of the companies hit had yet to install a critical Windows patch more than two months after it was released.
Other organizations in Spain known to be disrupted include telecom Vodafone Espana, the KPMG consultancy, banks BBVA and Santander, and power company Iberdrola. The Blackpool Victoria Hospital in the UK reportedly pleaded for patients to seek treatment only for life-threatening emergencies after Wcry crippled its network. Portugal Telecom has also reported being infected. Meanwhile, Barts Health Hospital in London is redirecting ambulances to other facilities. At least two train stations showed signs of infections according to display pictures published here and here.
According to an article posted by Madrid-based El Mundo, 85 percent of computers at Telefonica, Spain’s dominant telecom, are affected by the worm, although that figure has not been confirmed. Officials at Telefonica and Spanish energy companies Iberdrola and Gas Natural Fenosa have all instructed employees to shut down computers. While the paper confirmed an attack on Telefonica, it said it was not yet clear if the other two companies had been infected or if they ordered the shutdown as a preventative measure.
Wcry is demanding a ransom of $300 to $600 in Bitcoin to be paid by May 15, or, in the event that deadline is missed, a higher fee by May 19. The messages left on the screen say files will remain encrypted. It’s not yet clear if there are flaws in the encryption scheme that might allow the victims to restore the files without paying the ransom.
People who have yet to install the Microsoft fix—MS17-010—should do so right away. People should also be extremely suspicious of all e-mails they receive, particularly those that ask the recipient to open attached documents or click on Web links.
___________________________________
This post was updated repeatedly over the first six hours it was first published to report newly available information.
Further Reading:
NSA-leaking Shadow Brokers just dumped its most damaging release yet
Mysterious Microsoft patch killed 0-days released by NSA-leaking Shadow Brokers
 Dan Goodin is the Security Editor at Ars Technica, which he joined in 2012 after working for The Register, the Associated Press, Bloomberg News, and other publications. Email dan.goodin@arstechnica.com
Dan Goodin is the Security Editor at Ars Technica, which he joined in 2012 after working for The Register, the Associated Press, Bloomberg News, and other publications. Email dan.goodin@arstechnica.com
Go to Original – arstechnica.com
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.